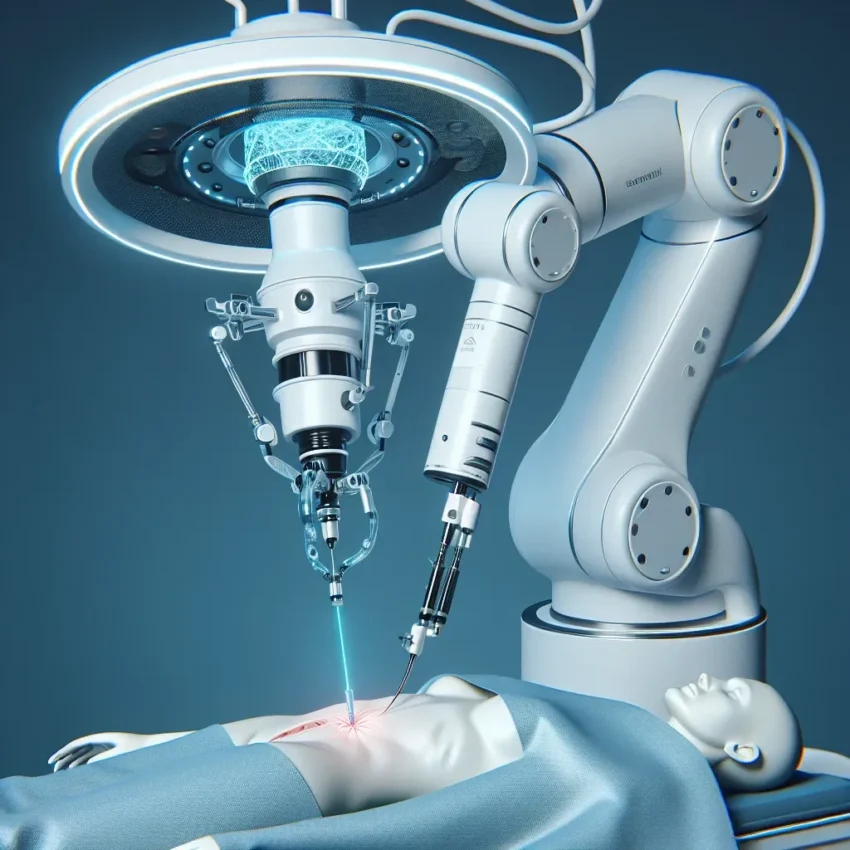
Introduction
The world of medicine is undergoing a transformation, driven by advancements in robotics and automation. One of the most exciting developments in this field is the use of autonomous biopsy insertion techniques, particularly through the application of mountable precision robots. These technologies promise to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of biopsy procedures, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Understanding Biopsy Procedures
A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves the extraction of a sample tissue from a living organism for diagnostic purposes. Traditionally, biopsies can be invasive and may require significant recovery time. The precision and effectiveness of biopsies are critical, as they directly impact diagnosis and subsequent treatment decisions.
Challenges in Traditional Biopsy Techniques
- Human Error: Despite the skill of healthcare professionals, human error can lead to complications, inaccurate results, or even unnecessary procedures.
- Invasive Nature: Many traditional biopsy methods are invasive, requiring significant patient recovery time and increasing the risk of complications.
- Limited Precision: Manual insertion techniques may lack the necessary precision, particularly in complex anatomical structures.
The Emergence of Autonomous Biopsy Insertion
Autonomous biopsy insertion using mountable precision robots represents a paradigm shift in how biopsies are performed. These robots are designed to operate independently, guided by sophisticated algorithms and real-time imaging technologies.
Key Features of Mountable Precision Robots
- High Accuracy: Utilizing advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans, these robots can identify the exact location of the target tissue with unprecedented accuracy.
- Minimally Invasive: Many autonomous systems are designed to minimize tissue damage, reducing recovery time and the risk of complications.
- Speed: Automated procedures can often be performed more quickly than traditional methods, allowing healthcare providers to increase their patient throughput.
How Autonomous Biopsy Insertion Works
The process of autonomous biopsy insertion involves several key steps:
1. Pre-Procedure Imaging
Before the procedure, high-resolution imaging is utilized to map the anatomy and identify the target tissue. This step is crucial for ensuring that the robotic system can accurately locate and retrieve the sample.
2. Robotic Calibration
Once the imaging is complete, the robotic system is calibrated according to the specific anatomical layout of the patient. This calibration is vital for ensuring that the robot can navigate to the target site without causing unnecessary damage to surrounding tissues.
3. Autonomous Insertion
With everything in place, the robot proceeds to perform the biopsy autonomously. Using advanced algorithms, it navigates to the target site, retrieves the tissue sample, and ensures minimal disruption to surrounding structures.
4. Post-Procedure Analysis
After the biopsy, the robot can also assist in analyzing the retrieved sample, potentially providing immediate feedback to healthcare providers.
Advantages of Autonomous Biopsy Insertion
The adoption of autonomous biopsy systems offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Accuracy: The precision of robotic systems significantly reduces the risk of human error, leading to more reliable diagnostic outcomes.
- Improved Patient Safety: By minimizing invasiveness, the likelihood of complications and recovery time is dramatically reduced.
- Increased Accessibility: Robotics can help hospitals and clinics handle more biopsies, making these services more accessible to patients.
Potential Disadvantages and Challenges
Despite the promising features and benefits, there are challenges that need to be addressed:
- Cost: The initial investment in robotic systems can be significant, which may limit their availability in some healthcare facilities.
- Training: Healthcare professionals must receive adequate training to work alongside these advanced systems, ensuring that they can effectively manage and interpret the robotic processes.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The integration of autonomous systems into medical practice raises various regulatory and ethical questions that must be addressed.
Future Predictions for Robotics in Biopsy Procedures
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see several trends in autonomous biopsy insertion:
- Integration with AI: The combination of artificial intelligence with robotic systems will likely enhance decision-making processes, making biopsies even more precise.
- Remote Biopsy Capabilities: The potential for remote-controlled robotic systems could allow specialists to perform biopsies from distant locations, increasing access to expert care.
- Personalized Medicine: As our understanding of genomics and pathology improves, biopsy procedures may become more tailored to individual patient needs and conditions.
Conclusion
The advent of autonomous biopsy insertion using mountable precision robots represents a significant leap forward in medical technology. While challenges remain, the potential for enhanced accuracy, improved patient safety, and increased accessibility makes this innovation a promising development in the field of medicine. As we continue to explore the capabilities of robotics and automation, the future of biopsy procedures looks brighter than ever.